Latest Topics in Electronics and Communication (ECE) for project, research, and thesis
Electronics
and Communication is an important field with respect to our daily life.
There are a number of good topics in electronics and communication
engineering (ECE) for thesis, research, and project. New developments
and research are going on in this field. It has made our life, even
more, easier and comfortable.
How?
Mobile
phones and Communication network have brought the world closer. All
thanks to electronics and communication engineers working towards the
development of these electrical products. Talking about academics,
students are often confused about which topic to choose in electronics
and communication for project, thesis or for the seminar. M.Tech
students find it even more difficult to choose a good master thesis
topics in communication engineering. Even after the choice of the topic
is made, students are unable to get proper thesis guidance and thesis assistance in ECE.
So what to do?
Here
are some of the latest and best topics in electronics and communication
which you can choose for your thesis, projects, and seminars for M.Tech
and Ph.D. You can get thesis help in any of these topics from the thesis guidance experts.
Latest Thesis and Research Topics in Electronics and Communication(ECE)
Following is the list of latest topics in Electronics and Communication(ECE) for the project, research and thesis:
- Bluetooth
- Fibre Optic Communication
- Embedded Systems
- Nanoelectronics
- VLSI
- OLED(Organic Light Emitting Diode)
- Zigbee Technology
- Human Area Network
- GPRS
- HSPA
Bluetooth
Bluetooth
is a low-power wireless technology used for exchange of data within a
short range. Bluetooth build a Personal Area Network(PAN) for exchange
of data between mobile devices. This technology was invented by Ericsson
in 1994. Bluetooth is based on radio technology known as
frequency-hopping spread spectrum. In this technology, the data is
transmitted in the form of packets. It is a very good topic for an
M.Tech thesis. Thesis help in
this topic can be taken from an expert in this field. Along with this
it is also a very good choice for major project in ECE. There are two
processes of Bluetooth technology:
- Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate(BR/ED)–It uses point-to-point topology to enable continuous wireless communication between two devices. The common example for this is wireless speakers.
- Low Energy(LE) – It uses multiple network topologies for communication which include point-to-point, mesh and broadcast. Point-to-point is for one to one device communication. Broadcast is for one to many device communication. Mesh is for many to many device communication.
Many
consumers are using this technology worldwide for streaming audio, data
exchange and broadcasting information. Bluetooth technology uses a
variety of protocols. The Bluetooth protocol stack is divided into two
parts: Controller Stack and the host stack.
The
controller stack is implemented in low-cost silicon devices that
contains Bluetooth radio and a microprocessor. The host stack is
implemented on the top of the operating system or as an installable
package on the operating system.

How Bluetooth technology works?
The
Bluetooth network is also known as Personal Area Network or Piconet in
which there are 2 to 8 devices. One is the master device that initiates
the communication while other are the slaves. The slave devices respond
to the action of the master device. The master device governs the
transmission between the slave devices. A slave device may begin
transmission only in an allotted time slot.
A scatternet is created when a device participates in more than one piconet.
Features of Bluetooth Technology
Following are some of the features of Bluetooth technology:
- Based on radio technology.
- Power consumption is less.
- There are fewer complications.
- Robust
- Cheaper
Applications of Bluetooth technology
- Wireless mobile phone headset.
- Bluetooth enabled laptops and Pcs.
- Wireless mouse and keyboard.
- Data transfer between mobile devices.
Disadvantages of Bluetooth Technology
Along with benefits, there are certain disadvantages of Bluetooth technology. Some of these are:
- High battery consumption.
- Security is poor.
- The data transfer is low.
- Lower bandwidth.
Fibre Optic Communication
For
transmission of large amount of data fibre optic communication is the
perfect choice. This type of communication is used to transmit data over
long distances over the computer network. This technology converts
electronic signals into light signals and the signals are transmitted
through the optical fibres. It is a very good choice for your M.Tech
thesis project. Thesis help in this topic can be taken from
professionals in this topic. Some of the characteristics of this type of
communication are:
- High bandwidth
- Long distance communication
- Less electromagnetic interference
- Transmission Security
How Fibre Optics Communication works?
Unlike
other form of communication, in fibre optics, the communication takes
place in the form of light signals. The components of fibre optics
communication are:
- Transmitter
- Receiver
- Light source
- Detector
The
transmitter receives input in the form of electrical signals which are
converted into light signals using a light source like LED and laser.
The light signal is transmitted using optic fibre cable to the receiver
where it is converted back into electric signals. The receiver consists
of a photodetector that measures the frequency of the optic field. The
wavelength near to the infrared is used for communication.

Photodetector – A
photodetector is a device that converts light signals into electric
signals. Two types of photodetectors mainly used in fibre optic
communication are PN photodiode and avalanche photodiode.
Advantages of fibre optics communication
Some of the advantages of fibre optics communication are:
- Higher transmission bandwidth
- Data transmission is higher
- Low power loss
- Higher Security
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference
Disadvantages
- High installation cost
- More number of repeaters
- More maintenance is required
Embedded Systems
Embedded
Systems are the type of physical hardware systems with software
embedded in that. This system is microprocessor or microcontroller-based
and can be independent or can be a part of larger system. This system
is specifically designed to perform some tasks. It is a hot topic for
thesis, project ad for seminar. If you know little about this topic you
can also take thesis guidance for this topic. Following are the three
components of embedded systems:
- Hardware
- Software
- Real-Time Operating System
Characteristics of Embedded Systems
The characteristics of the embedded systems are:
- Single Functionality – Embedded Systems are specifically designed to perform a single task.
- Tightly Constrained – Embedded Systems are based on constraints like design, cost , size, and power.
- Reactive – Embedded Systems are reactive in nature i.e. they instantaneously react to any changes in nature.
- Based on microprocessor – Embedded Systems are microprocessor and microcontroller based.
- Memory – These systems have ROM(Read Only Memory) embedded in that as there is no need of secondary memory.
- Connectivity – These systems have peripherals connected to them for input and output.

What an Embedded System consists of?
The basic structure of an embedded system consists of the following components:
Sensor – To measure the quantity of a system by converting it into electrical signals.
A/D Converter – It is required to convert analog to digital signals.
Processor – It processes the data and stores it into memory.
D/A Converter – It converts digital to analog signals.
Actuator – An actuator compares the output of the D/A converter to the expected output.
Advantages of Embedded Systems
- These systems can be easily customized.
- These have low power consumption.
- The cost is comparatively low.
- The power is enhanced.
Disadvantages of Embedded Systems
- High efforts in development
- Marketing is not easy.
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics
is a field that deals with the use of nanotechnology in electrical
components. On the other hand, nanotechnology is a branch of engineering
that deals with the matter at an atomic and molecular level.
Nanoelectronics more or less is based on the transistors. The
transistors used here have size lesser than 1000 nanometers. These are
so small that there is separate study to understand the inter atomic
interactions as well as quantum mechanical properties. These transistors
are designed through nanotechnology and are very much different from
the traditional transistors.
The
work that a nanoelectronic device can do depends upon its size. With
increase in volume, the power of the device will increase. The
development in this field is in progress as there are some limitations
of it when used in real world.
Different approaches to nanotechnology
The different approaches to nanotechnology are:
- Nanofabrication
- Nanomaterials Electronics
- Molecular Electronics
- Nanoionics
- Nanophotonics

Applications of Nanoelectronics
Certain development and applications have been made in this field of nanotechnology which are as follows:
- Nanoradio – These will have nanoprocessors for its working with high speed and performance. Carbon nanotubes are being used in this application.
- Nanocomputers – Traditional computers will be replaced by nanocomputers for higher performance and speed. Detailed research is being carried out in this field.
- Medical Diagnostics – Nanoelectronic devices can detect biomolecules and thus will help in medical diagnostics.
- Energy Production – Research is being conducted to create energy efficient solar cells, galvanic cells and fuel cells.
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration)
VLSI
is a process to create Integrated Circuits(IC) by combining together
thousands of transistors on a single chip. Microprocessor is an example
of VLSI. Before the development of VLSI, the Integrated Circuits had
limited functionality and performance. VLSI gives the ability to add
CPU, RAM, ROM and other such functions on a single chip.
Due to this, the electronics industry has recorded a commendable growth.

Design of VLSI
VLSI
maily consists of front-end design and back-end design. Front-end
design is the digital design while back-end design is the
CMOS(Complememtary metal-oxide semiconductor) library design. The steps
followed while designing a VLSI are:
- Problem Specification – In this step, various parameters are studied like size, cost, performance and functionality.
- Architecture – In this step, specifications like floating point unit, ALU, RISC/CISC and cache size are studied.
- Functional Design – The functional unit along with the input and output are defined in this step using a block diagram.
- Logical Design – The main logic of the system is designed at this step. Other developments in this step include boolean expression, register allocation, control flow and word width.
- Design of the Circuit – The circuit is designed after the logical design by the use of gates and transistors.
- Physical Design – The complete layout of the system is designed at this step through geometrical representation.
- Packaging – The final product is obtained after putting together all the chips into a single printed circuit board.
Advantages of VLSI
The advantages of VLSI are:
- Size of the circuit is reduced.
- Cost of the device is reduced.
- Increase in overall performance and speed.
- Higher reliability
- Find its use in almost every field from computers to medicines.
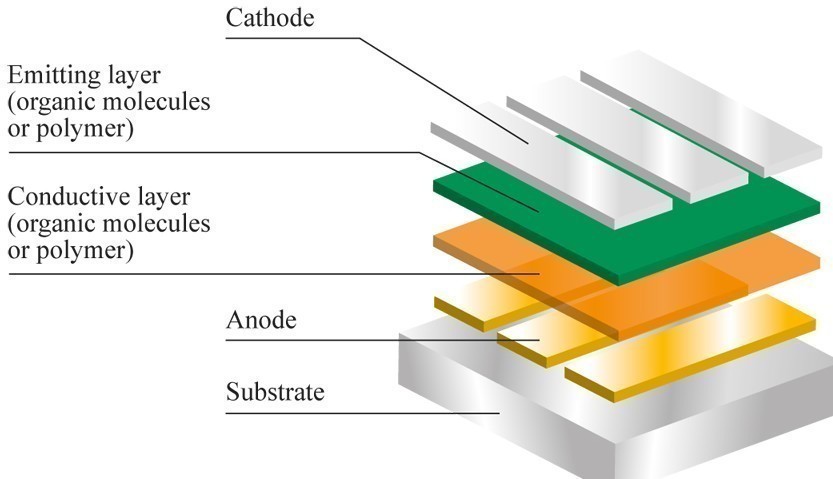
OLED(Organic Light Emitting Diode)
OLED
is a type of LED( Light Emitting Diode) with a small change that the
component that produces light is made up of a thin layer of organic
compounds. This organic semiconductor layer is situated between the two
electrodes. It is mainly used for flat panel displays, mobile devices,
and smartphones. There are two types of OLEDs :
- Based on small molecules
- Using polymers
Working of OLEDs
Organic
LED work almost in the same way as traditional LEDs with some changes.
In this instead of n-type and p-type semiconductors, organic molecules
are used to produce electrons and holes. There are 6 layers of OLED. The
top layer is known as the seal while the bottom layer is called the
substrate. There are two terminals between the top and the bottom layers
– anode(positive terminal) and cathode(negative terminal). In between
these terminals, there are the organic layers one is the emissive layer
and the other one is the conductive layer.
A
voltage is connected to the anode and the cathode. Electricity starts
flowing and the cathode starts receiving electrons while the cathode
starts losing them. As the electrons are added, the emissive layer
starts becoming negatively charged while the conductive layer starts
becoming positively charged. The positively charged holes starts jumping
towards the emissive layer. When the positive hole meets the negatively
charged electron ,a photon is produced which is a particle of light.
Advantages of OLEDs
- These are superior to LCDs.
- These are thinner, lighter and flexible.
- The respond time is faster.
- They produce true colors with better viewing angle.
Disadvantages of OLEDs
- These have comparatively less life time than the LCDs.
- The organic molecules degrade over the time.
- These are very sensitive to water.
ZigBee Technology
ZigBee is an IEEE 802.15.4 based communication system designed for wireless personal area network.
This standard allows the physical and media access control layer(MAC)
to handle various devices at a very low-data rate. The main
characteristics of this technology is that it is low powered and low
cost. It controls and manages application within a range of 10-100
metres. Moreover, it is less expensive than the Bluetooth and Wifi.

Architecture of ZigBee
This system consist of the following three devices:
- ZigBee Coordinator
- Router
- End Device
The
ZigBee coordinator acts as the bridge and the root of the whole
network. It handles and stores the information by performing some data
operations. The ZigBee routers are the intermediatory device that allows
data to pass to and from other devices. The end device communicates
with the parent node. The ZigBee protocol consists of the following 5
layers:
- Physical Layer – This layer performs the modulation and demodulation operation.
- MAC Layer – This layer access different networks using CSMA to check for reliable transmission of data.
- Network Layer – This layer looks after all the operations related to the network.
- Application Support Sub-Layer – This layer matches two devices according to their services and needs.
- Application Framework – This layer provides two types of data services. One is the key value pair and the other one is the generic messages service.
ZigBee Operating Modes
There two modes of operation in ZigBee:
- Non-beacon – In this mode, there is no monitoring of the incoming data by the coordinators and the routers.
- Beacon – In this mode, the active state of the incoming data is continuously monitored by the coordinators and routers thereby consuming more power.
Applications of ZigBee Technology
ZigBee finds its application in the following fields:
- Industrial Automation
- Home Automation
- Smart Metering
- Smart Grid Monitoring
Human Area Network
Human
Area Network is a wireless network also referred to as RedTacton that
uses the human body as a medium for high-speed transmission. It is
different from other wireless and infrared technologies in the sense
that it uses tiny electric field emitted on the surface of the human
body. It is a very good topic under ece thesis topics list.
The
human body forms a transmission path whenever a part of it comes into
contact with the RedTacton transceiver. Body surface can be hands, legs,
arm, feet or face. It can work through clothes and shoes. Whenever the
physical contact between the transceiver and the human body is lost,
communication ends.
It has the following three main features:
- The communication can be triggered by human movements like touching, gripping, walking, sitting, and stepping for obtaining data.
- The transmission speed is not depleted when many people are communication at the same time as the transmission path is human body surface.
- Conductors and dielectrics can be used along with the human body.

Working of Human Area Network
The
approach of Human Area Network is different from other networks. It
does not use electromagnetic waves or light waves for data transmission.
Instead, it uses weak electric signals on the human body for
transmission. It works as follows:
- The RedTacton transmitter generates a weak electric signal on the human body surface.
- Any changes caused by the transmitter to the electric field is sensed by the RedTacton receiver.
- RedTacton depends upon the principle that the changes in the weak electric field can cause a change in the optical properties of an electro-optic crystal.
- These changes are detected using a laser and the result is produced in the form of electrical signals.
RedTacton uses CSMA/CD(Carrier Sense with Multiple Access with Collision Detection) protocols for transmission.
GPRS
GPRS
stands for General Packet Radio Services. It is a packet-based service
for 2G and 3G mobile communication. It is standardized under European
Telecommunications Standards Institute(ETSI). It provides higher data
rates for Internet on mobile phones. It is based on GSM(Global System
for Mobile) communication and provides additional services on
circuit-switched connections and Short Message Service(SMS). It is
another popular topic for final year project, thesis, and seminar.
GPRS has the following main features:
- It has lesser cost than the circuit-switched services as the communication channels are shared.
- It provides variable throughput and latency.
- It provides data rates of 56-114 kbps.
- It supports IP, PPP, and X.25 packet-based protocol.

Services offered by GPRS include:
- SMS(Short Messaging Service)
- Internet Access
- MMS(Multimedia Messaging Service)
- Push-to-talk service
- Instant Messaging
- Point-to-point(P2P) and point-to-multipoint(P2M) services
HSPA
It
stands for High-Speed Packet Access. It is a combination of two
technologies named HSDPA and HSUPA for uplink and downlink. This
provides high-speed data access. It can provide download speed up to 384
kbps. It uses WCDMA protocols and improves the performance of the
existing 3G mobile communication. Students looking for ece project ideas
can work on this topic.
Components of HSPA
Following are the two main components of HSPA providing a link between the base station and the user:
- HSDPA(High-speed Downlink Packet Access) – HSDPA is used to provide support for packet data and a data rate of 14 Mbps. Also, it helps in reducing delays.
- HSUPA(High-speed Uplink Packet Access) – It also provides data support with improved features along with data rate of 5.74 Mbps.

Benefits of HSPA
There are a number of benefits of HSPA but following are the significant ones:
- HSPA uses a higher order of modulation for data to be transmitted at a higher rate.
- It uses a Shorter Transmission Time Interval(TTI) to reduce the round trip time and reduction in latency.
- It uses a shared channel for transmission which provides a great level of efficiency.
- To maximize the channel usage, link adaption is used.
- Fast Node B scheduling is used with adaptive coding and modulation to respond to the constantly varying radio channel and interference.
Techsparks offer thesis and research help in electronics and communication (ECE). You can contact us on this number 91-7696666022 or email us at techsparks2013@gmail.com for any help in all the latest topics in electronics and communication. You can also fill the query form on the website.



